
Basiswechsel Einen Vektor bezüglich einer neuen Basis darstellen (ausführlichere Version) YouTube
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history.
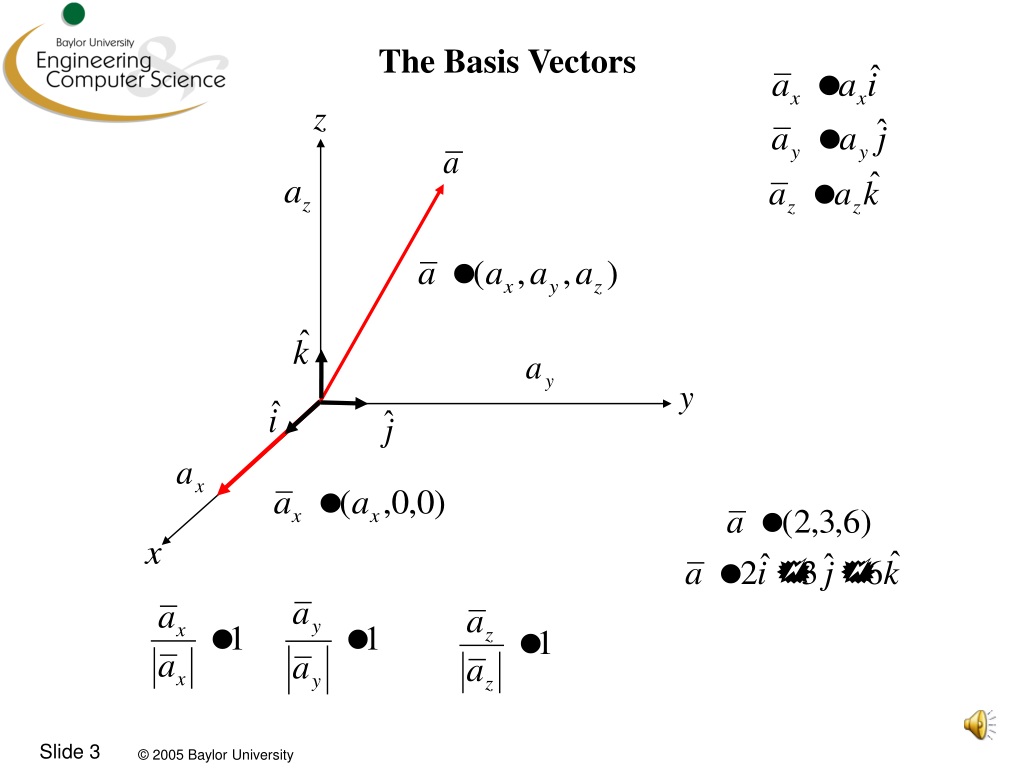
PPT Fundamentals of Engineering Analysis EGR 1302 Unit Vectors and Basis Vectors PowerPoint
Meskipun basis dari sebuah ruang vektor tidak tunggal, tetapi basis-basis tersebut mempunyai banyak anggota yang sama, sehingga dimensi ruang vektor bersifat tunggal. Teorema Mengenai Basis dan Dimensi. Pada bagian ini, kita akan membahas beberapa teorema yang berkaitan dengan basis dan dimensi ruang vektor. Mari memulai dengan ketunggalan.

Vektor Basis dan Vektor Posisi, Matematika Kelas X YouTube
However this would imply that we could find a basis of \(\mathbb{P}_2\) of more than three polynomials. This contradicts the result of Example \(\PageIndex{5}\) in which we determined the dimension of \(\mathbb{P}_2\) is three. Therefore if these vectors are linearly independent they must also form a spanning set and thus a basis for \(\mathbb.
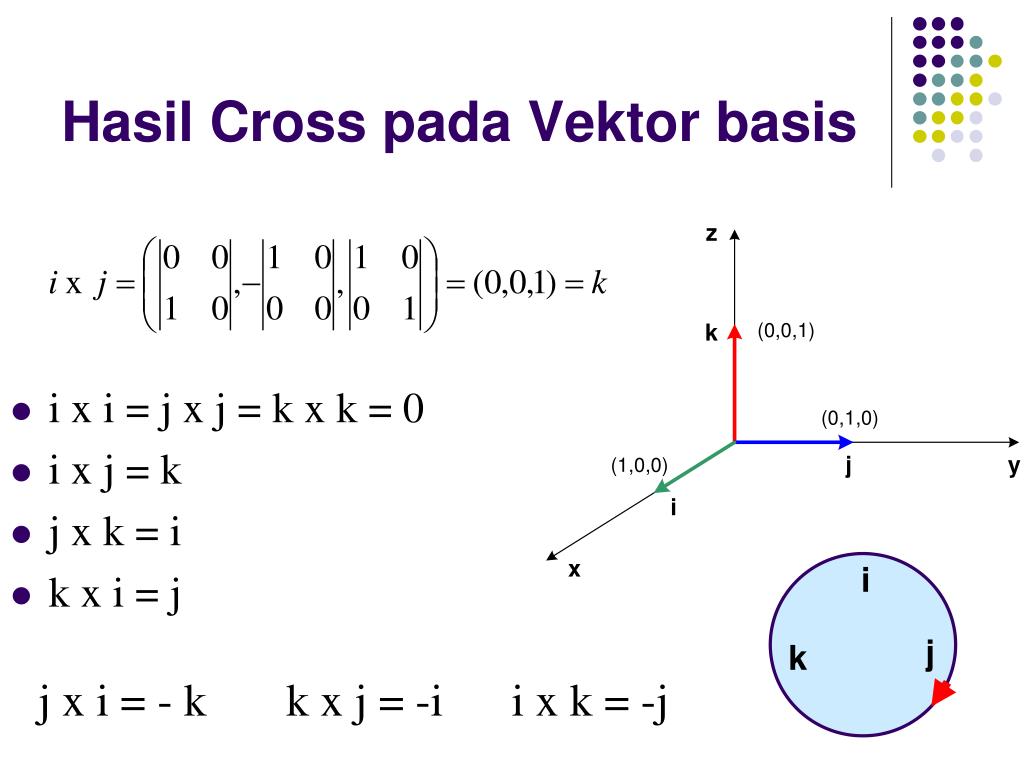
PPT VEKTOR PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6322812
Since V has a basis with two vectors, it has dimension two: it is a plane. Figure 2.7.3 : A picture of the plane V and its basis B = {v1, v2}. Note that B spans V and is linearly independent. This example is somewhat contrived, in that we will learn systematic methods for verifying that a subset is a basis.
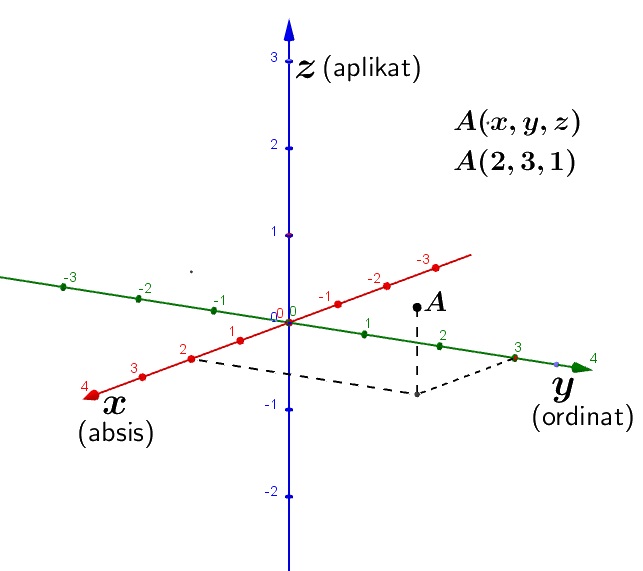
Soal Dan Pembahasan Vektor Matematika Kelas 10 Duvall Voutter
An orthogonal matrix is a square matrix whose columns form an orthonormal set of vectors. If a matrix is rectangular, but its columns still form an orthonormal set of vectors, then we call it an orthonormal matrix. When a matrix is orthogonal, we know that its transpose is the same as its inverse.

Vektor • einfach erklärt mit Beispielen · [mit Video]
A basis for a polynomial vector space P = {p1,p2,.,pn} P = { p 1, p 2,., p n } is a set of vectors (polynomials in this case) that spans the space, and is linearly independent. Take for example, S = {1, x,x2}. S = { 1, x, x 2 }. and one vector in S S cannot be written as a multiple of the other two. The vector space {1, x,x2,x2 + 1} { 1.

Was ist eine Basis? Vektorräume YouTube
At the point P shown below, first draw the rectangular basis vectors x ^ and , y ^, then draw the polar basis vectors r ^ and . ϕ ^. Finally, use your drawing to work out the relationship between these basis vectors. Make sure that your formula works for every quadrant. Note: You can move the point P in the figures below. Figure 1.12.1. Polar.
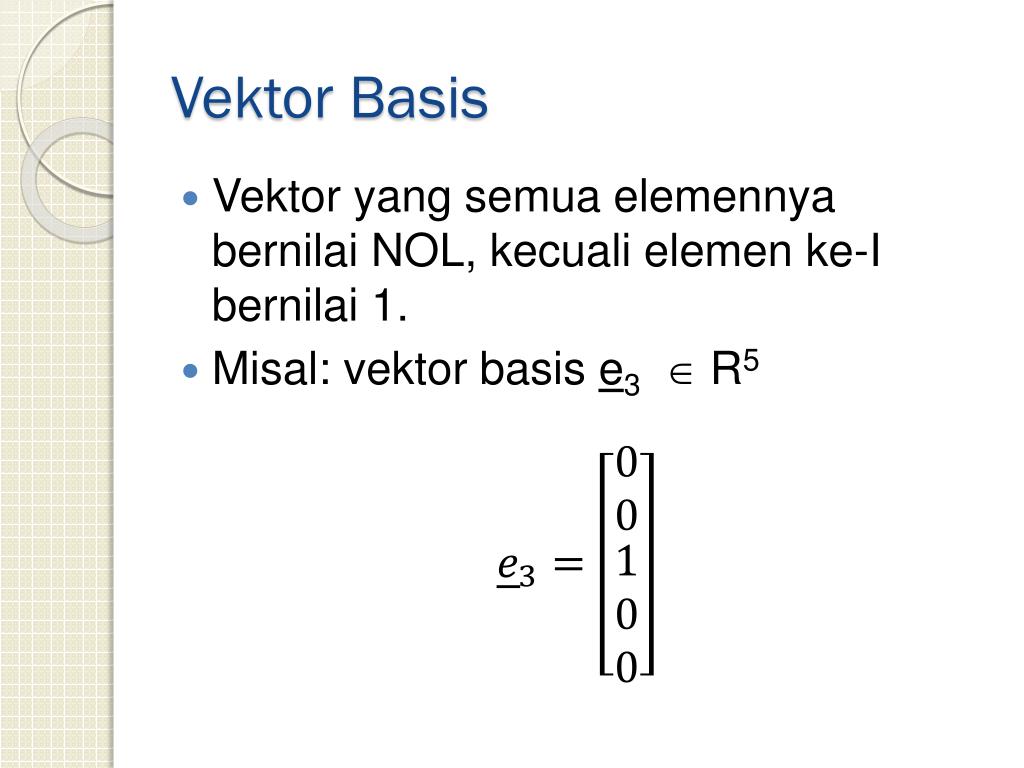
PPT Konsep Vektor dan Matriks PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6086680
A basis vector in an n-dimensional vector space is one of any chosen set of n vectors in the space forming a vector basis, i.e., having the property that every vector in the space can be written uniquely as a linear combination of them. For example, in the Euclidean plane, the unit vectors e^->_1=(1,0) and e^->_2=(0,1) form a vector basis since for any point (x,y), (x,y)=xe_1+ye_2, so for this.
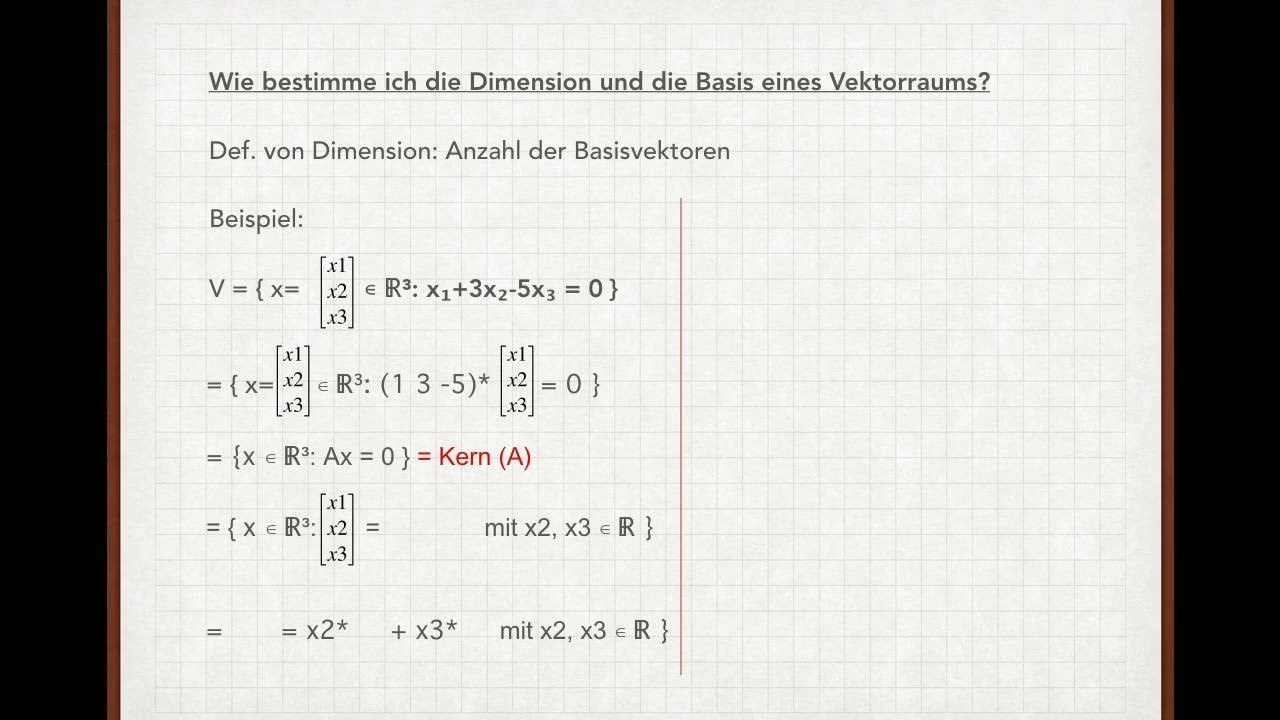
Basis und Dimension eines Vektorraums berechnen (mit Beispiel) YouTube
The most important attribute of a basis is the ability to write every vector in the space in a unique way in terms of the basis vectors. To see why this is so, let B = { v 1, v 2,., v r} be a basis for a vector space V. Since a basis must span V, every vector v in V can be written in at least one way as a linear combination of the vectors in B.

Basis dan Dimensi Ruang Vektor YouTube
Let V be a vector space. Suppose V has a basis. S = {v1, v2, . . . , vn} consisiting of n vectors. Then, we say n is the dimension of V and write dim(V ) = n. If V consists of the zero vector only, then the dimension of V is defined to be zero. We have. From above example dim(Rn) = n. From above example dim(P3) = 4.

Vektor basis dari vektor c = AB jika diketahui titiktiti...
Vektor basis merupakan vektor satuan yang saling tegak lurus. Dalam vektor ruang dua dimensi memiliki dua vektor basis yaitu dan . Sedangkan dalam tiga dimensi memiliki tiga vektor basis yaitu , , dan . Vektor di R^2. Panjang segmen garis yang menyatakan vektor atau dinotasikan sebagai Panjang vektor sebagai:

Basis Vectors YouTube
Linear algebra is a branch of mathematics that allows us to define and perform operations on higher-dimensional coordinates and plane interactions in a concise way. Its main focus is on linear equation systems. In linear algebra, a basis vector refers to a vector that forms part of a basis for a vector space.

(Matriks & Ruang Vektor)_Basis dan Dimensi YouTube
Blog Koma - Pada artikel ini kita akan membahas materi Vektor Basis Normal Standar yang merupakan salah satu dari bagian "materi vektor tingkat SMA".Pada artikel sebelumnya tentang "Pengertian Vektor dan Penulisannya", sebuah vektor dapat kita sajikan atau tulis dalam bentuk vektor baris atau vektor kolom atau dalam vektor basis $ \vec{i} , \, \vec{j} , \, \vec{k} $.

PPT Bab 4 vektor PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5063500
A vector basis of a vector space is defined as a subset of vectors in that are linearly independent and span . Consequently, if is a list of vectors in , then these vectors form a vector basis if and only if every can be uniquely written as. (1) where ,., are elements of the base field. When the base field is the reals so that for , the.

Vektor dalam bidang 02 _ Hasil kali titik Vektor basis YouTube
A basis of a vector space is a set of vectors in that space that can be used as coordinates for it. The two conditions such a set must satisfy in order to be considered a basis are the set must span the vector space; the set must be linearly independent. A set that satisfies these two conditions has the property that each vector may be expressed as a finite sum of multiples of.
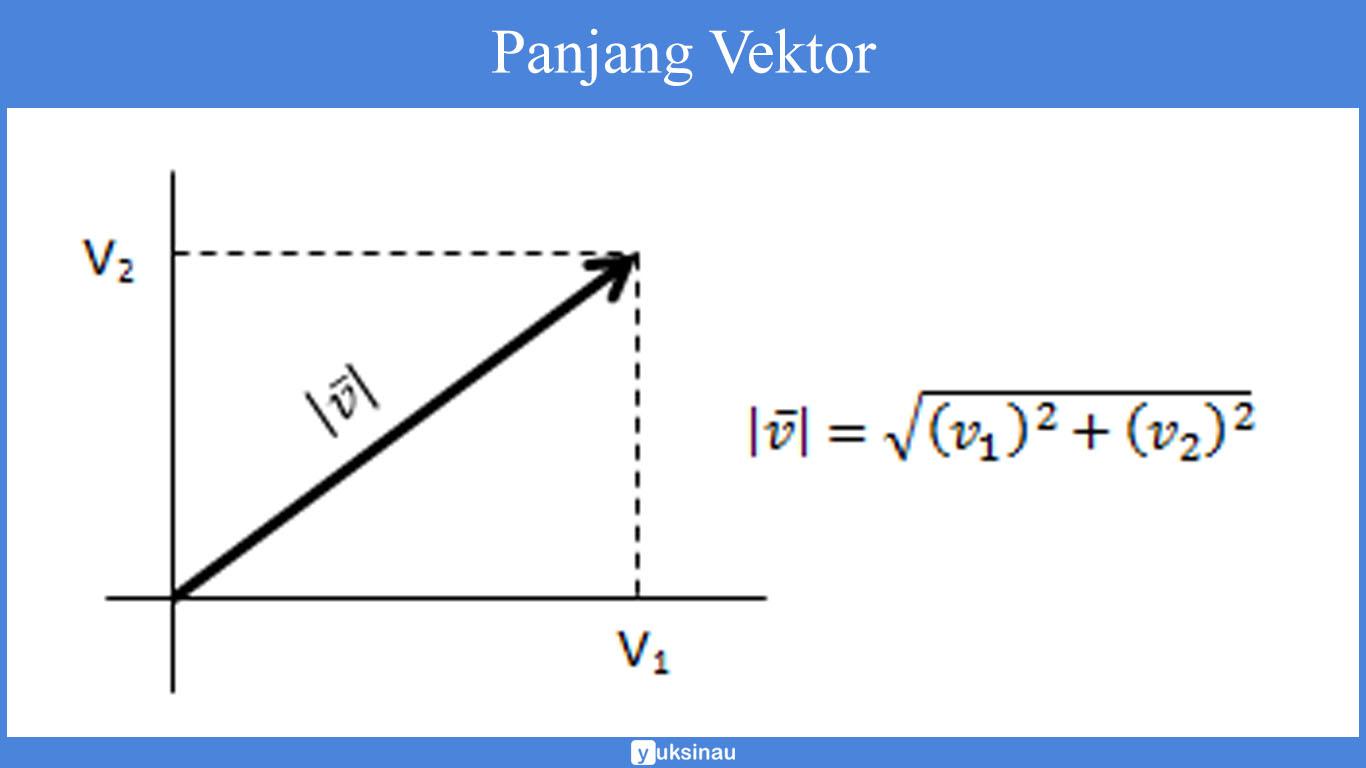
Operasi Vektor dan Contoh Soalnya
In mathematics, the standard basis (also called natural basis or canonical basis) of a coordinate vector space (such as or ) is the set of vectors, each of whose components are all zero, except one that equals 1. [1] For example, in the case of the Euclidean plane formed by the pairs (x, y) of real numbers, the standard basis is formed by the.