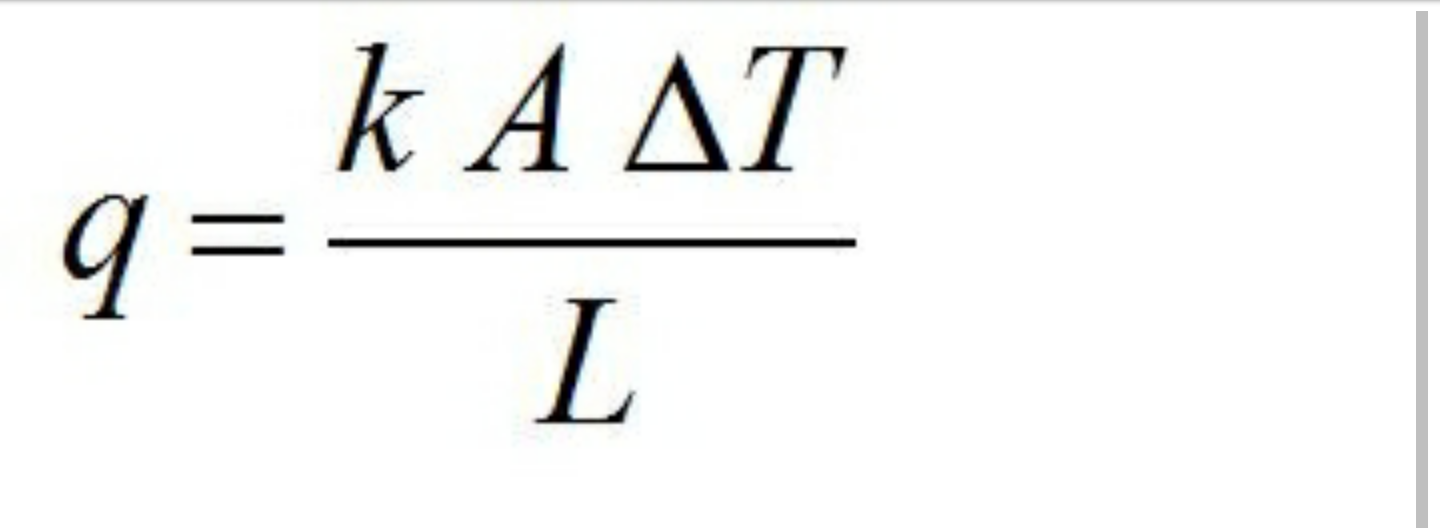
√ Rumus Delta T
Follow the steps below to use the Moody equation to estimate the Darcy friction factor. Step 1: Enter the hydraulic diameter of the pipe or conduit. Step 2: Input the surface roughness of the pipe. Note that the equation is only valid for k/D ratio less than 0.01. Step 3: Insert the Reynold's number for the flow regime.
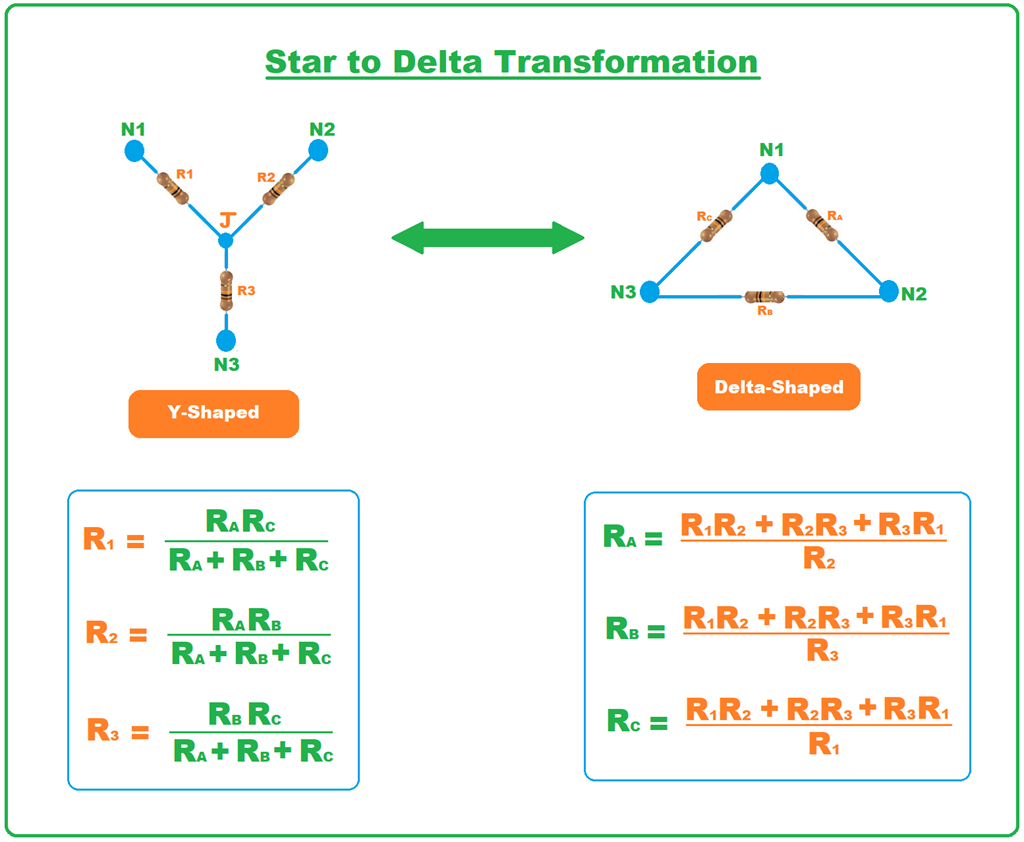
Transformasi Star Delta Transformasi Rumus Dan Diagram Belajar Cloud Sexiz Pix
F = m * delta p / delta t, where delta t is the 1 second the ball is in contact with the wall during the 'bounce' and delta p is the same as above: 2v. We get F = m * 2v / 1 = 2*mv. Clearly the method shown in the video gives a much smaller force than when considering time as only the time when the object is applying the force to the wall.

Tren Gaya Rumus Daya Listrik Phase My XXX Hot Girl
Simply put, Delta P refers to the change in pressure between two points. It is often used to describe fluid flow and can be applied in various fields such as engineering, physiology, and thermodynamics. The concept of delta P is crucial in understanding how fluids move and behave in different environments. For instance, knowing the difference.

√ Rumus Delta T
Exercise 19.7.1 19.7. 1. Calculate ΔG Δ G for the reaction of nitric oxide with oxygen to give nitrogen dioxide under these conditions: T = 50°C, P NO = 0.0100 atm, PO2 P O 2 = 0.200 atm, and PNO2 = 1.00 ×10−4atm P NO 2 = 1.00 × 10 − 4 a t m. The value of ΔGo Δ G o for this reaction is −72.5 kJ/mol of O 2.

apa perbedaan molalitas dan molaritas Brainly.co.id
Pressure Loss. The pressure loss (or major loss ) in a pipe, tube or duct can be calculated with the Darcy-Weisbach equation. Δp major_loss = λ (l / d h ) (ρ f v 2 / 2) (1) where. Δp major_loss = major (friction) pressure loss in fluid flow (Pa (N/m 2 ), psf (lb/ft 2 ) ) λ = Darcy-Weisbach friction coefficient. l = length of duct or pipe.

Gambar Dan Rumus Fisika Tentang Gerak Gravitasi, Hukum Newton, Fisika, Sains PNG Transparent
Berikut penjelasan kelompok sifat koligatif: 1. Koligatif Larutan - Penurunan tekanan uap jenuh (Δ Tp ) Penurunan tekanan uap jenuh adalah selisih tekanan uap pelarut murni dan tekanan uap larutan . tabel penurunan tekanan uap jenuh larutan non elektrolit dan elektrolit ↓. Uraian. Larutah non elektrolit.

Laju Reaksi Pengertian Rumus Dan Contoh Soal Laju Reaksi Jempol Kimia The Best Porn Website
3 Answers. Sorted by: 3. Certainly, you agree dH =CPdT d H = C P d T if we're at constant pressure. If H H and CP C P don't actually depend on pressure, then you can use this equation regardless of whether pressure changes. However, to determine CP C P and H H you first need an equation of state (such as PV = NkT P V = N k T ).

Behavior for \(\Delta P\) with neutrino CP phase given by \(\delta =0\)... Download Scientific
The corrected log mean temperature difference for the heat exchanger is: \scriptsize \qquad \Delta T_ {\mathrm {LMTD}} = 0.91 * 24.667 = 22.443\ \degree\text {C} ΔT LMTD = 0.91 ∗ 24.667 = 22.443 °C. Alternatively, you can also input the log mean temperature difference in the calculator and some inlet or outlet temperatures to find the rest.
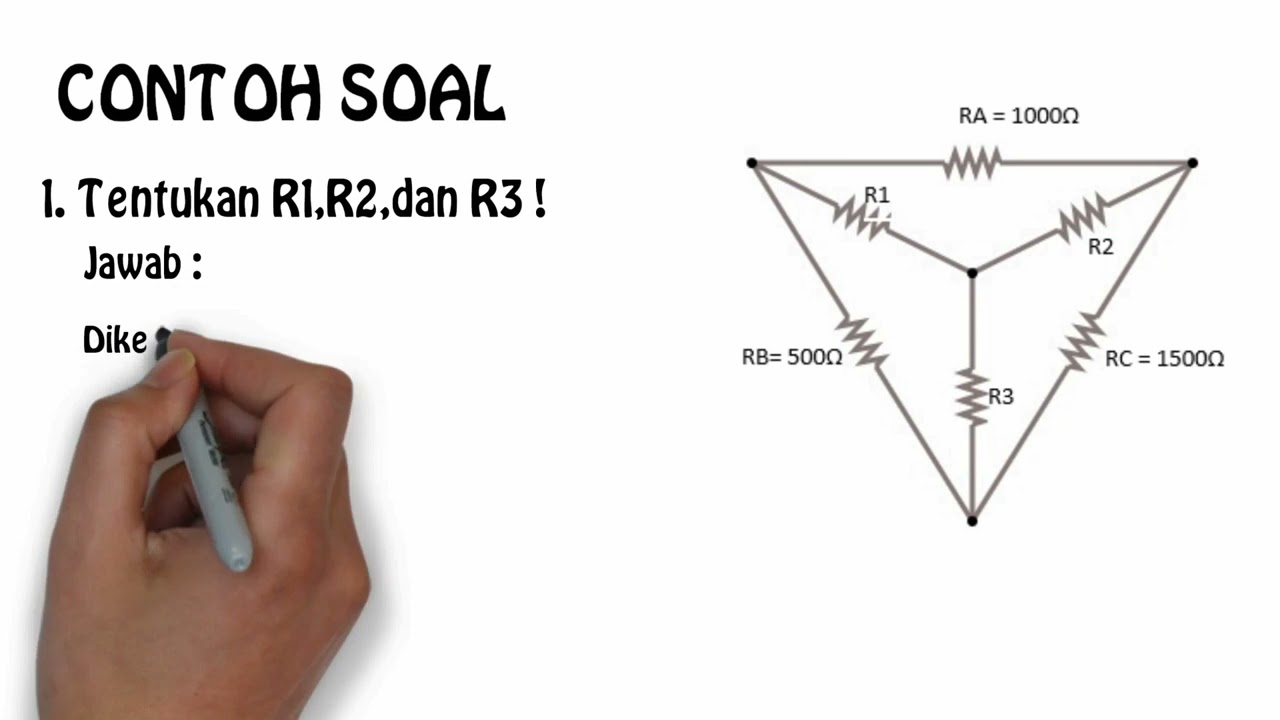
cara menghitung rumus star delta kelistrikan YouTube
The mass flow rate m [kg/s] is a measurement of the amount of water flowing around the hot water loop.. The specific heat capacity Cp [kJ/kg/°C] is a thermodynamic property specific of the fluid used to transfer heat. We could manipulate the specific heat capacity only by changing the fluid used in the loop. Water is a good fluid choice for cost and safety considerations.
Kumpulan rumusfisikasma
Rumus. Koefisien elastisitas dapat dirumuskan dengan: Elastisitas permintaan; E d = -delta Q/ delta P x P/Q atau Elastisitas penawaran; E s = delta Q/delta P x P/Q. E = Persentase perubahan permintaan atau penawaran/Persentase perubahan harga. Sifat elastisitas barang atau jasa terbagi menjadi beberapa yaitu: Elastis = koefisien lebih dari 1

Download Contoh Soal Penurunan Tekanan Uap Background
Cv (t) = Cv0* (1-t/tau)^1.5. where, Cv (t) is the flow coefficient as a function of time. Cv0 is the full open Cv value. t is the time and it goes from zero to tau. tau is the total stroke time. If the stroke is linear over time, then (1-t/tau) is simply the fraction of the full stroke. at t=0, the valve is full open; at t=tau, the valve is.
5 Tahapan Reaksi Kimia kabarmedia.github.io
Mechanical Engineering. Mechanical Engineering questions and answers. The volume flow rate of flow, Q, through a pipe containing a slowly moving fluid is given by the equation Q = pi R^4 Delta p/8 mu l where R is the pipe radius. Delta p is the pressure drop along the pipe, mu is dynamic viscosity, and l is the length of the pipe.

Rumus Hukum Termodinamika 1 / Contoh Soal Hukum Termodinamika 1 Materiipa Com Yaitu 1 kalori
Dynamic pressure. In fluid dynamics, dynamic pressure (denoted by q or Q and sometimes called velocity pressure) is the quantity defined by: [1] u is the flow speed in m/s. It can be thought of as the fluid's kinetic energy per unit volume . For incompressible flow, the dynamic pressure of a fluid is the difference between its total pressure.
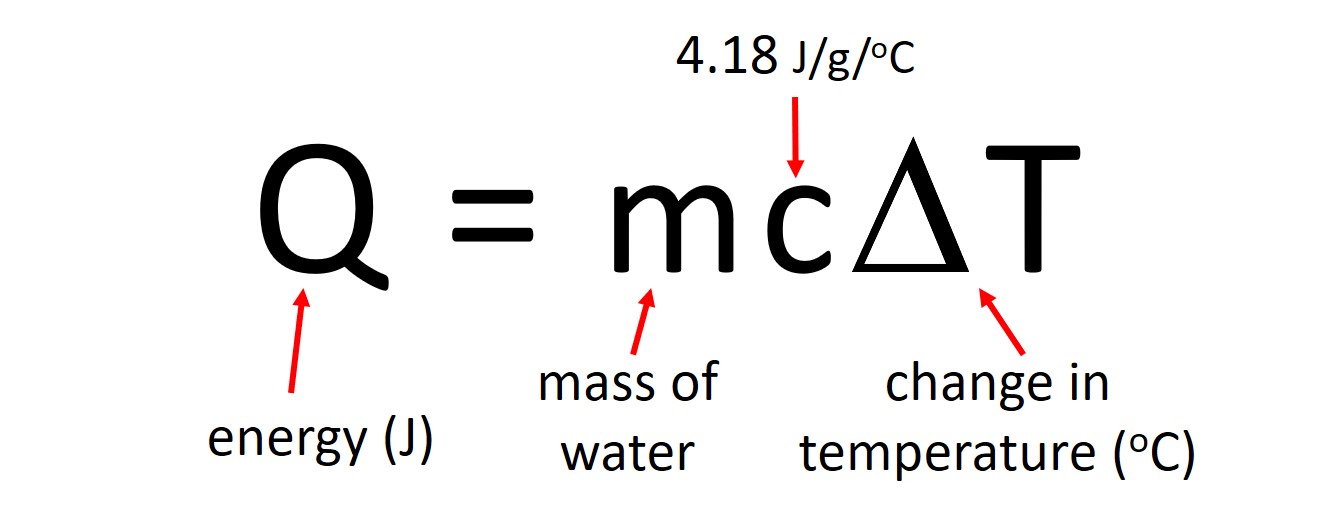
3.1 3.8 Energetics
Usaha yang dilakukan oleh gas pada tekanan tetap: Keterangan: p: Besarnya tekanan (atm) Δ V {\displaystyle \Delta V} : Perubahan volume (liter) Rumus umum usaha yang dilakukan gas: Penghitungan energi dalam: Gas monoatomik: Δ U = 3 2 n × R × Δ T = 3 2 n × R × ( T 2 − T 1 ) {\displaystyle \Delta U= {\frac {3} {2}}n\times R\times \Delta.

Diketahui data entalpi pembentukan standar delta Hf C4H1...
In chemical reactions involving the changes in thermodynamic quantities, a variation on this equation is often encountered: ΔGchange in free energy = ΔHchange in enthalpy − TΔS(temperature) change in entropy. Example 1.1. Calculate ∆G at 290 K for the following reaction: 2NO(g) + O 2(g) → 2NO 2(g) Given. ∆H = -120 kJ.
Contoh soal interferensi gelombang
In physics, the Young-Laplace equation (/ l ə ˈ p l ɑː s /) is an algebraic equation that describes the capillary pressure difference sustained across the interface between two static fluids, such as water and air, due to the phenomenon of surface tension or wall tension, although use of the latter is only applicable if assuming that the wall is very thin.