+Microscope.jpg)
Discovering of the Bacteria Medical Education
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, who lived in the Netherlands between 1632 and 1723, was an amateur in science and lacked any type of formal university training. His experiments with microscopy design and function led him to become an international authority on microscopy and he was granted the honor of Fellowship in the Royal Society in 1680.
Gutopia A Microbial Paradise Science and Food
Anton van Leeuwenhoek lived to the ripe old age of 90 and by his death in 1723, he had made many significant scientific discoveries. 1. Early Life. Van Leeuwenhoek had a tumultuous childhood. He was born in Delft in the Netherlands to a basket weaver father and a mother from a wealthy family of brewers. He had four older sisters.

ANTONI VAN LEEUWENHOEK Dutch inventor of the microscope 1632 1723 Stock Photo Alamy
Van Leeuwenhoek' on the lid, and an aalkijker from Russia. However, there is no evidence to link the two events which happened almost 200 years apart. It might (as speculated by Dobell 1932) have happened, but de Gorter's microscopes might equally easily have come from the auction, although the catalogue does not mention a red morocco case.

CURIOSIDADES CIENTÍFICAS LEEUWENHOEK. Un nuevo mundo microscópico.
Pioneering microbiologist Antoni van Leeuwenhoek made the best microscopes of the pre-industrial era with methods that he kept secret. But the first full-3D scans of two of his instruments reveal.

Leeuwenhoek's microscope Stock Image H505/0048 Science Photo Library
This paper discusses the scientific instruments made and used by the microscopist Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723). The immediate cause of our study was the discovery of an overlooked document.

Leeuwenhoek's microscope. Download Scientific Diagram
Three hundred years ago the Dutch microscopist Antoni van Leeuwenhoek died. He had been corresponding with the Royal Society for fifty years. Leeuwenhoek, born in Delft in the Netherlands in 1632, developed himself into one of the most prolific early microscopists. He made his own lenses and small hand-held microscopes which were more versatile.

Los microscopios de Van Leeuwenhoek
This paper discusses the scientific instruments made and used by the microscopist Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723). The immediate cause of our study was the discovery of an overlooked document from the Delft archive: an inventory of the possessions that were left in 1745 after the death of Leeuwenhoek's daughter Maria.

Anton Van Leeuwenhoek Discovery
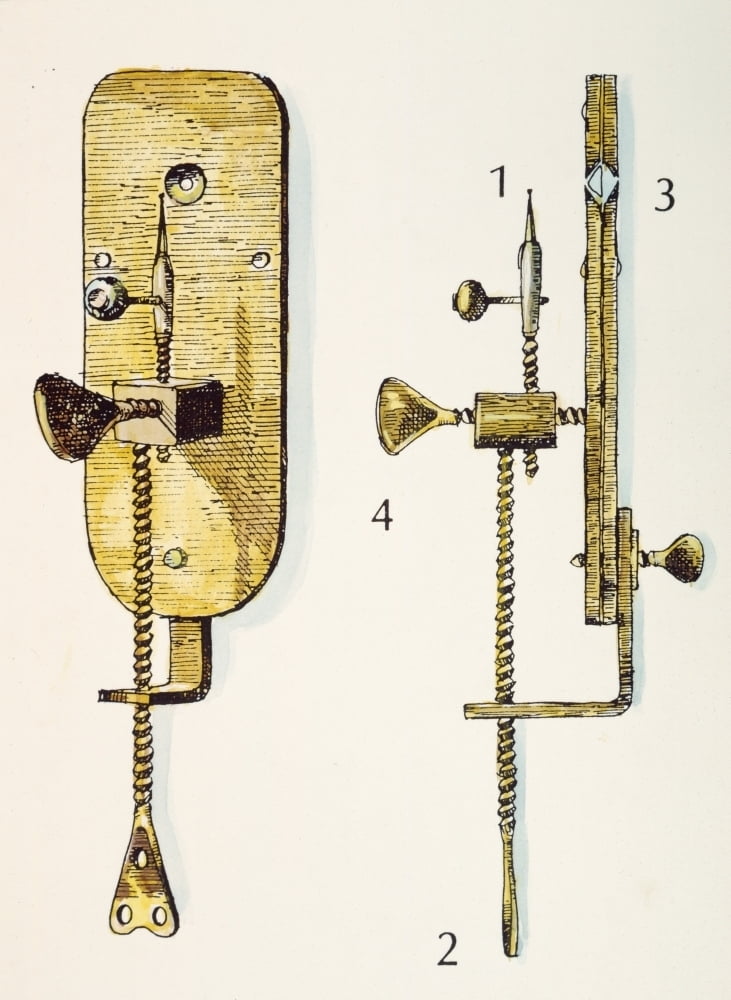
It seems that Hooke's aversion to simple single-lens microscopes passed on down the generations, but not his appreciation of their merits. The compound microscope, with its refractive aberrations, became the tool of choice, and Leeuwenhoek's microscopes were quietly forgotten, their oblivion hastened by Leeuwenhoek's own secrecy, notwithstanding his gift of 13 microscopes, with corresponding.
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek /N(16321723). Dutch Naturalist. One Of Leeuwenhoek'S Microscopes (1) The
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) was born in Delft, where he lived for most of his life. Leeuwenhoek attended a grammar school and was taught by his uncle before taking up an apprenticeship with an Amsterdam linen-draper. His first encounter with microscopy would have been examining cloth samples with a magnifying glass.

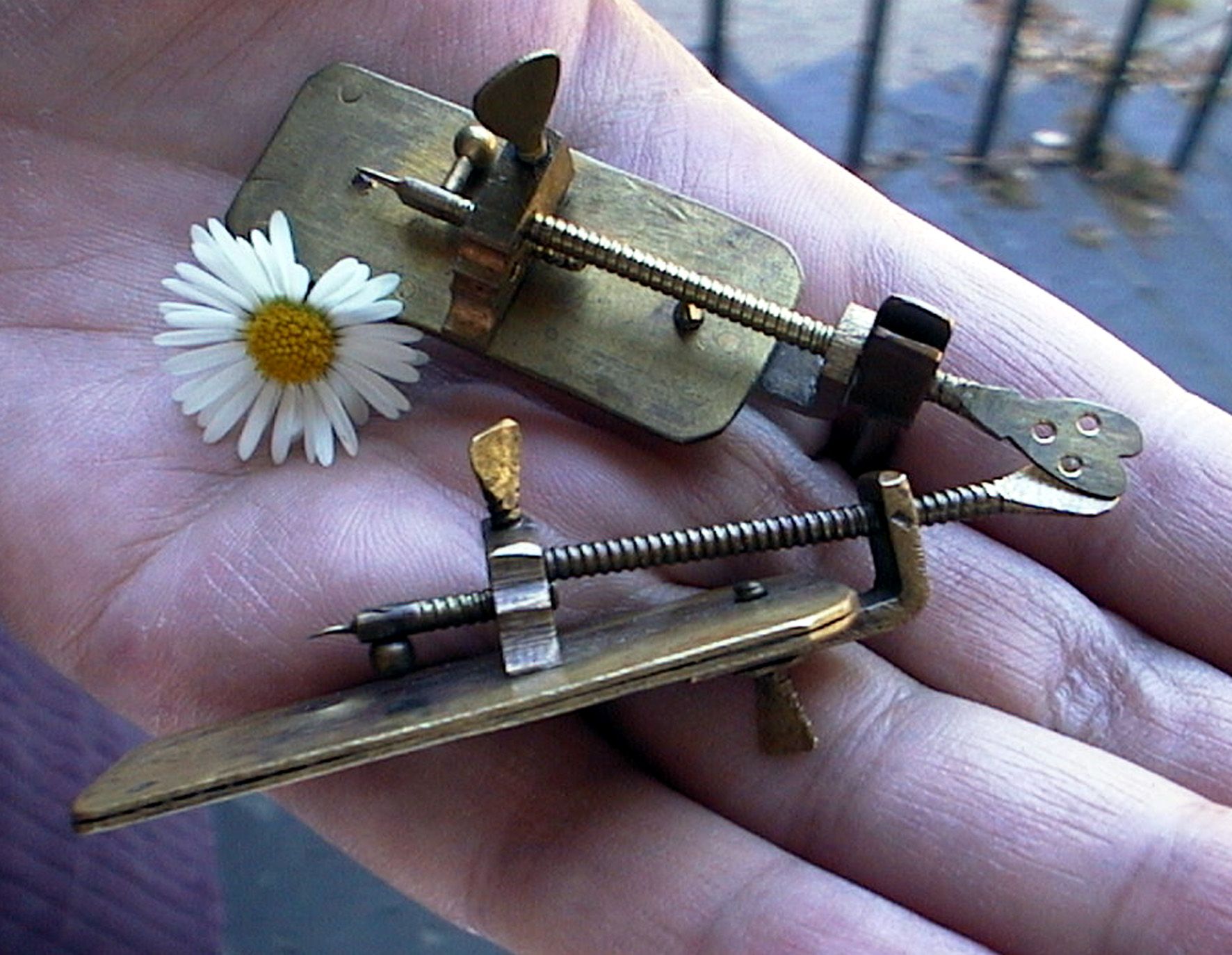
Finding more van Leeuwenhoek microscopes… Delft Microbiology
Mikroskop von Antoni van Leeuwenhoek Bildquelle: Deutsches Museum. Van Leeuwenhoek beschritt einen anderen Weg: Sein Mikroskop bestand nur aus einer Linse. Im Prinzip gilt: je kugelförmiger die Linse, um so geringer die Brennweite und um so stärker die Vergrößerung. Nur: niemand konnte bis dahin so kleine und exakte Kugellinsen herstellen.

Leeuwenhoek's Lucky Break Water flask, Flask, Oil lamps
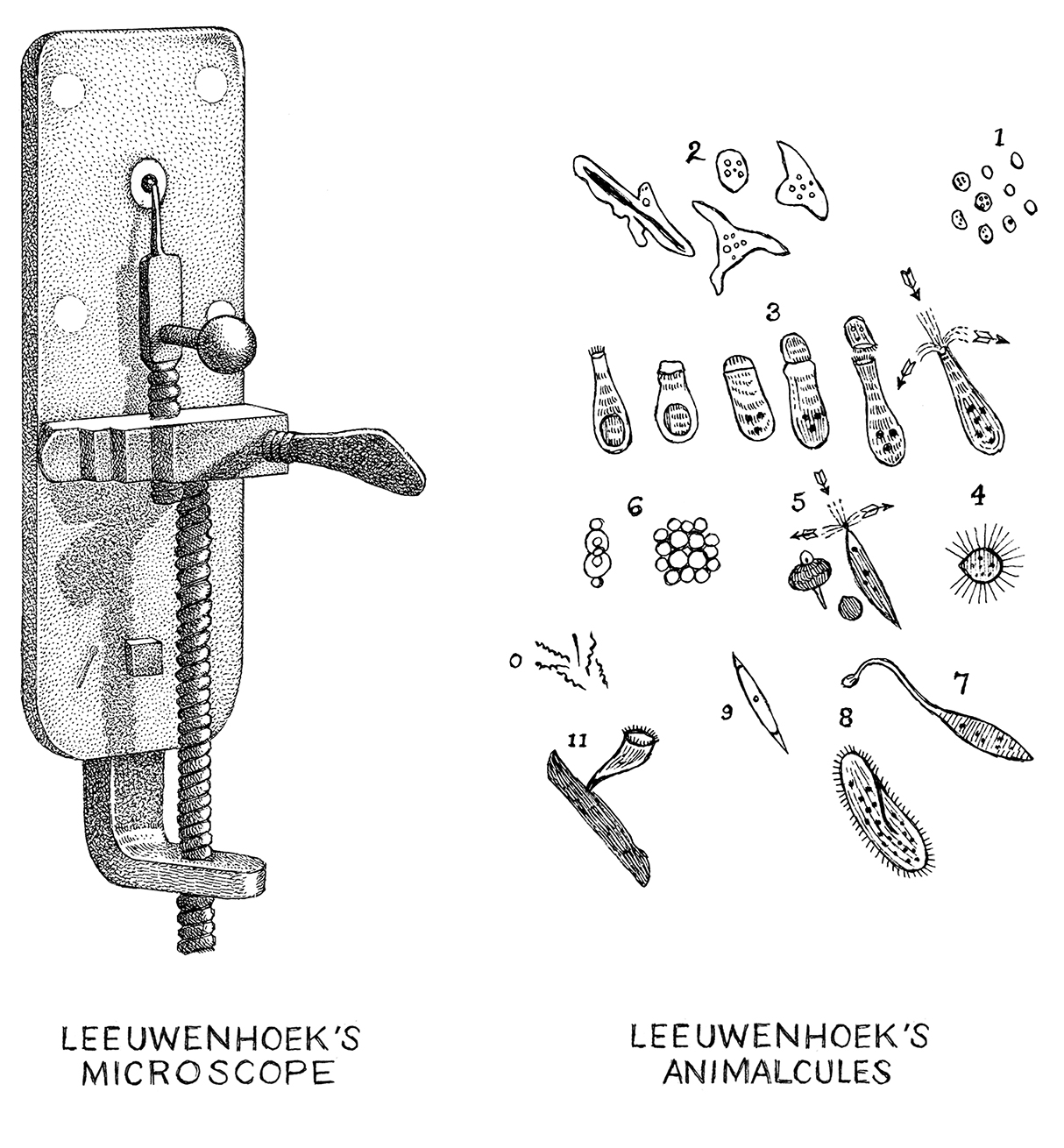
The Dutch scientist and entrepreneur Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) was the first to discover and describe microorganisms (protists, bacteria), living beings he characterized as "animalcules" (little animals). Using single-lensed microscopes created for his own, private research, he was able to see and draw microbes for the first.

Origin of Life Scienceandsf A Blog Published by Robert A. Lawler
Van Leeuwenhoek also contributed to science in one other way. In the final year of his life, he described the disease that took his life. Van Leeuwenhoek suffered from uncontrollable contractions of the diaphram, a condition now known as Van Leeuwenhoek disease. He died of the disease, also called diaphragmatic flutter, on August 30, 1723, in.

van Leeuwenhoek microscope
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (born October 24, 1632, Delft, Netherlands—died August 26, 1723, Delft) Dutch microscopist who was the first to observe bacteria and protozoa.His researches on lower animals refuted the doctrine of spontaneous generation, and his observations helped lay the foundations for the sciences of bacteriology and protozoology.. Early life and career

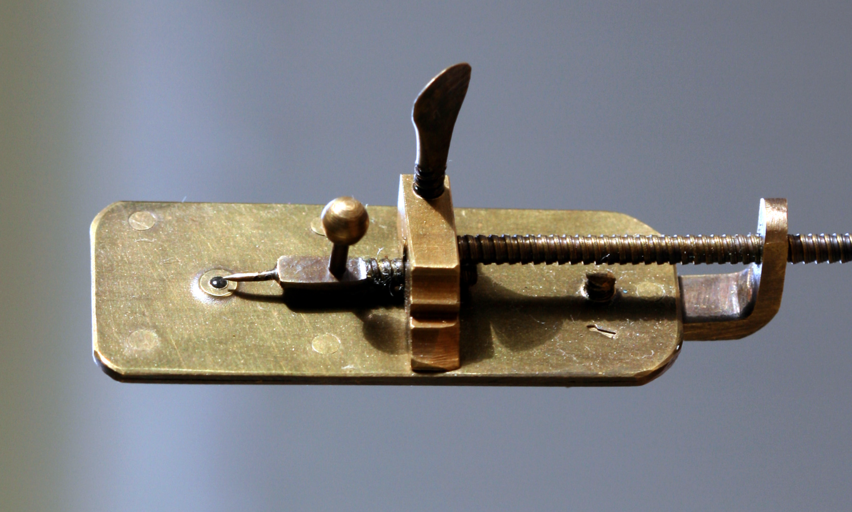
FileLeeuwenhoek Microscope.png Wikipedia
The seventeenth-century Dutch microscopist, Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, was the first man to make a protracted study of microscopical objects, and, unlike his contemporary Robert Hooke, he viewed by transmitted light. Leeuwenhoek made over 500 of his own, curious, simple microscopes, but now only nine are known to exist..
Mystery of Van Leeuwenhoek's microscope lens is partly solved DutchNews.nl
Van Leeuwenhoek's descriptions of finding samples have supported the principle that repeating historic experiments ("living history") is useful provided that care is taken with experimental detail. Speculation and theory are not sufficient. For example, there is at least one modern illustration of Van Leeuwenhoek holding his microscope to.

leeuwenhoek microscope 3d model
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) was the most important microscopist of the Scientific Revolution.The Dutchman made over 500 microscopes, many with a magnification far superior to contemporary models. His discoveries include bacteria, protozoa, red blood cells, spermatozoa, and how minute insects and parasites reproduce.