
Understanding Linux File Permissions The Complete Guide Edumotivation
This nifty online chmod calculator lets you calculate the file permissions in absolute and symbolic modes in a few clicks. Chmod Calculator: Calculate Linux File Permissions Chmod Calculator Just select the permissions that you want for your files and hit the Calculate button. The permissions are displayed under the calculate button. Owner Read:

pokyny čistič výlet permission calculator počiatočné rozrezaný meč
Chmod calculator generates command in number format for file and directory permissions in Unix and Linux. If you are working on Unix, Linux server then permissions are a very important and difficult task. Our chmod calculator generates file permissions for owner, group, and the public in number (744) and symbolic (rwxr--r--) notation formats.
Linux File Permissions — chmod(numeric) calculator by Divya Bhushan
HOW DOES CHMOD CALCULATOR WORK. The chmod calculator is an intelligent online tool that takes care of all the complex calculations of the perfect chmod entry for the type of permission you require. The well-structured and integrated calculator takes all the burden off your shoulder and provides you with the specific entry for your permission.

Study Linux permissions in 2021 IP ON WIRE
What is chmod command? The name chmod is an abbreviation of change mode. It's a command used in Unix and Unix-type operating systems to change the permissions of files or directories. There are different permissions for three classes: the user, the group, and the others. But who is who?

karavána snazzy Paradajka permission linux calculator záves uhol vonkajšie
The concept of Linux permissions calculator revolves around three main entities: user, group, and public. Owner Permissions Every file and directory in Linux is associated with a user. The user permissions define what actions the owner of the file or directory can perform.
Linux permissions tables Reffffference
Explain Linux File Permissions and Ownership Explained with Examples Linux file permissions explained in simpler terms. Also learn how to change the file permissions and ownership in Linux in this detailed beginner's guide. Aug 17, 2018 — Abhishek Prakash Linux File Permissions and Ownership Explained with Examples

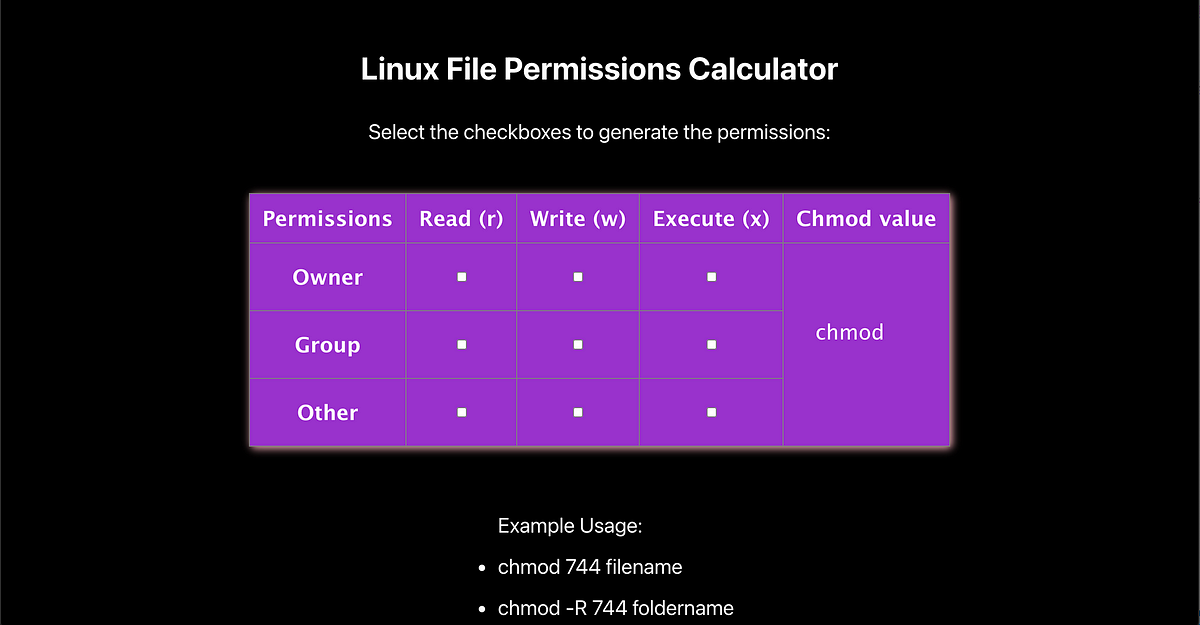
Linux File Permissions Calculator
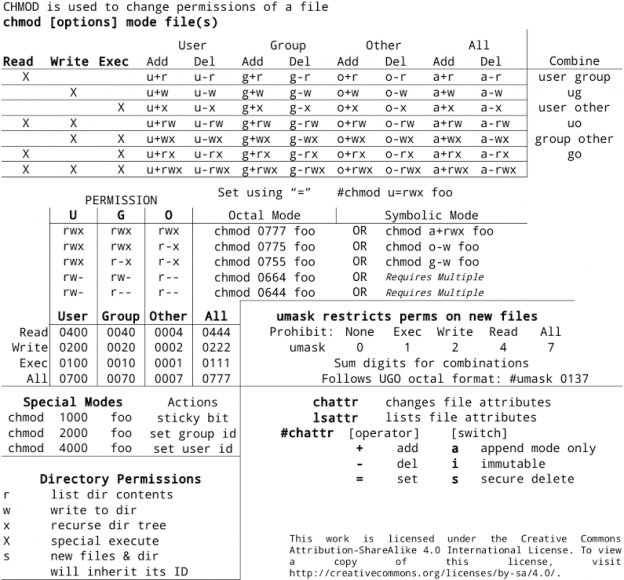
The chmod command is used to control who can access files and directories on Unix and Unix-like systems. It allows you to specify three types of permissions for each file or directory: read, write, and execute. Change access permissions, change mode. read (r) → allows users to open and read the file's contents.

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
The basic Linux permissions model works by associating each system file with an owner and a group and assigning permission access rights for three different classes of users: The file owner. The group members. Others (everybody else). File ownership can be changed using the chown and chgrp commands.
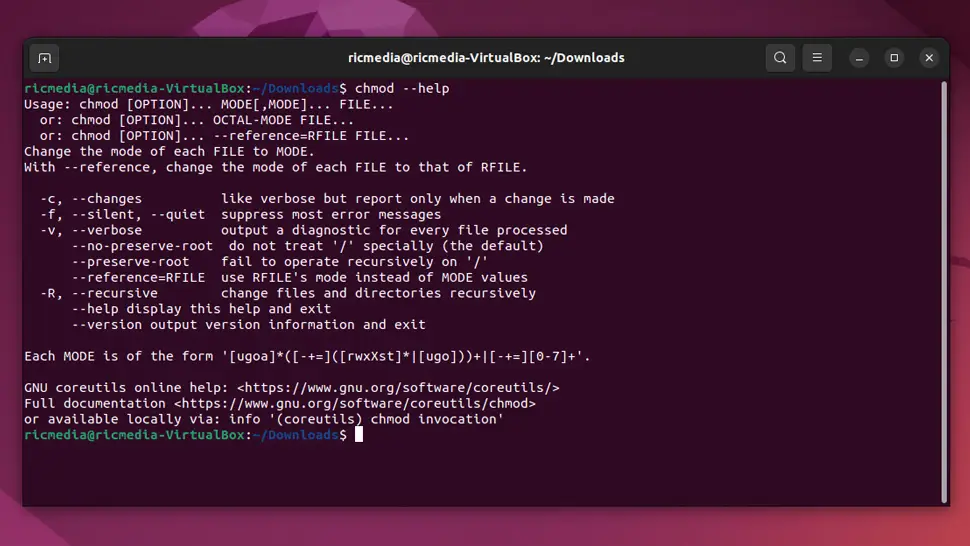
A Guide to Linux File Permissions and the chmod Command Ricmedia
File permissions are core to the security model used by Linux systems. They determine who can access files and directories on a system and how. This article provides an overview of Linux file permissions, how they work, and how to change them. File Permissions | Into the Terminal 02 Watch on How do you view Linux file permissions?
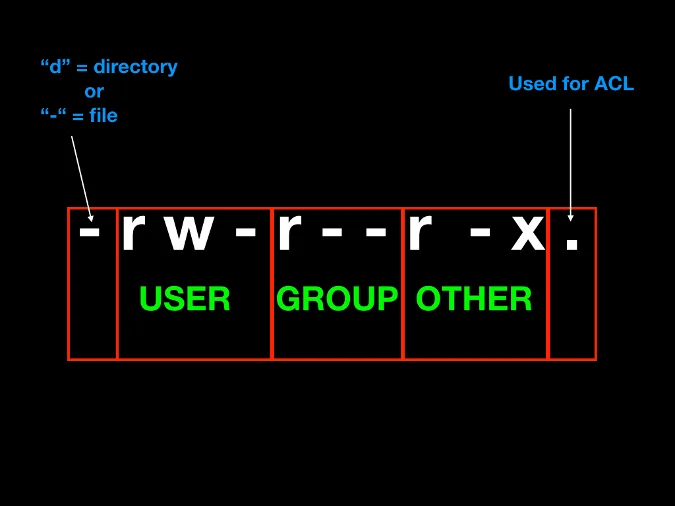
A beginner's guide to Linux permissions
There are three specific UNIX/Linux file system permissions - read ( r ), write ( w ), and execute ( x ). Permissions are grouped into three sets or triads, each defining access for different scope or class: user/owner ( u ), group ( g ), and everyone else/others ( o ). Permissions can be presented either in numeric (octal) or symbolic notations.

Linux file permissions 101 The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
Chmod calculator allows you to quickly generate permissions in numerical and symbolic formats. All extra options are included (recursive, sticky, etc). You'll be ready to copy paste your chmod command into your terminal in seconds. Use the octal CHMOD Command: chmod -R 777 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command: chmod -R a+rwx folder_name

Linux permissions reset qustacme
SUID. SGID. Sticky. Special. Numeric Change permissions Recursively change permissions. Understanding and using file permissions on unix systems. Includes an easy-to-use calculator for filesystem permissions.

A beginner's guide to Linux permissions
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. 777) or symbolic notation (e.g. rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats. File Permissions

Linux File Permissions Calculator
About Chmod Calculator. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in unix or unix-like systems such as linux or ubuntu.. How it Works? Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. 777) or symbolic notation (e.g. rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats.
25+ Linux Permission Calculator SahlaSandeep
Chmod Calculator is an online utility to convert Linux permissions for files or directories on servers between different formats (symbolic, numeric). Easy to use: Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. 644) or symbolic notation (e.g. rw-rw-r--) to see its value in other formats.

A beginner's guide to Linux permissions
What Are File Permissions? A file permission is a set of rules determining who has access to a particular file. There are three main categories of file permissions: Read, Write, Execute. Why Do You Need Them? If you're using Linux, macOS, or Windows, you'll probably need them at some point.